Ch3ch2oh + o2 balanced equation – Delving into the realm of chemistry, we encounter the intriguing topic of balanced chemical equations. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the secrets behind the balanced equation for the reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2, exploring its significance and delving into the intricate details of reactants, products, and reaction mechanisms.
This equation, meticulously crafted to represent the chemical transformation, serves as a roadmap guiding us through the intricacies of the reaction. It provides a quantitative understanding of the substances involved, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element remains constant throughout the reaction.
Balanced Chemical Equation: Ch3ch2oh + O2 Balanced Equation

A balanced chemical equation is a representation of a chemical reaction in which the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side of the equation equals the number of atoms of that element on the products’ side. This ensures that the law of conservation of mass is upheld, as no atoms are lost or gained during the reaction.
Step-by-Step Balancing
To balance the equation for the reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2, we need to adjust the stoichiometric coefficients in front of each chemical formula until the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides.
- First, we start with the unbalanced equation: CH3CH2OH + O2 → CO2 + H2O
- We count the number of atoms of each element on both sides:
- C: 2 on the reactants’ side, 1 on the products’ side
- H: 6 on the reactants’ side, 2 on the products’ side
- O: 2 on the reactants’ side, 3 on the products’ side
- To balance the carbon atoms, we add a coefficient of 2 in front of CO2: CH3CH2OH + O2 → 2CO2 + H2O
- Now, we count the atoms again:
- C: 2 on both sides
- H: 6 on the reactants’ side, 2 on the products’ side
- O: 4 on the reactants’ side, 4 on the products’ side
- To balance the hydrogen atoms, we add a coefficient of 3 in front of H2O: CH3CH2OH + O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
- Finally, we count the atoms one last time:
- C: 2 on both sides
- H: 6 on both sides
- O: 4 on both sides
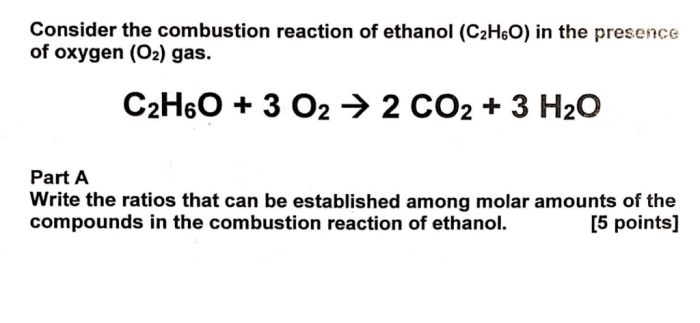
The balanced equation is now: CH3CH2OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Significance
Balanced chemical equations are essential for several reasons:
- They allow us to determine the stoichiometry of a reaction, which is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products.
- They help us predict the products of a reaction and the relative amounts of each product that will be formed.
- They enable us to calculate the amount of reactants or products needed or produced in a reaction.
Reactants and Products

In the combustion reaction between CH3CH2OH (ethanol) and O2 (oxygen), the reactants are ethanol and oxygen, and the products are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Ethanol (CH3CH2OH):A colorless, flammable liquid with a characteristic odor. It is soluble in water and has a boiling point of 78.5 °C.
- Oxygen (O2):A colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas. It is essential for life and supports combustion.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):A colorless, odorless, and non-flammable gas. It is heavier than air and can cause suffocation if inhaled in large amounts.
- Water (H2O):A colorless, odorless, and tasteless liquid. It is the most abundant substance on Earth and is essential for life.
Role in the Reaction
- Ethanol:The fuel that reacts with oxygen to produce energy.
- Oxygen:The oxidizer that reacts with ethanol to produce carbon dioxide and water.
- Carbon Dioxide:A waste product of the reaction.
- Water:A byproduct of the reaction.
Reaction Conditions
The reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2 is an exothermic process that requires specific conditions to proceed efficiently.
The balanced equation for the combustion of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) with oxygen (O2) is a fundamental concept in chemistry. While delving into this topic, it’s worth exploring the captivating story of Frida Kahlo’s life in the “Con Frida en el Altiplano” PDF . This book offers a glimpse into the remarkable journey of an extraordinary artist.
Returning to our scientific exploration, the balanced equation for CH3CH2OH + O2 serves as a valuable tool for understanding the chemical reactions involved in combustion.
Temperature:The optimal temperature for this reaction is between 250-300°C. At lower temperatures, the reaction rate is slow, while at higher temperatures, the reactants may decompose or undergo side reactions. Pressure:The reaction can occur at atmospheric pressure or slightly elevated pressures.
Increased pressure can shift the equilibrium towards the products, but it has a relatively small effect on the reaction rate. Catalyst:A catalyst is not typically required for this reaction, as it proceeds readily under the optimal conditions described above.
However, certain catalysts, such as metal oxides or transition metals, can enhance the reaction rate and selectivity.
Safety Considerations
Both CH3CH2OH and O2 are flammable substances. The reaction should be carried out in a well-ventilated area, away from sources of ignition. Proper personal protective equipment, such as gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat, should be worn during the experiment.
Reaction Mechanism

The reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2 is a complex process that involves several steps. The detailed reaction mechanism is as follows:
Initiation
The reaction is initiated by the formation of hydroxyl radicals (OH) from the decomposition of oxygen molecules (O2).
OH + O2 → HO2
Propagation
The hydroxyl radicals react with CH3CH2OH to form a hydroperoxyl radical (HO2CH2CH2OH). The hydroperoxyl radical can then react with another oxygen molecule to form a peroxyl radical (CH3CH2OO).
HO2CH2CH2OH + O2 → CH3CH2OO + HO2
The peroxyl radical can then react with another CH3CH2OH molecule to form two molecules of CH3CHO.
CH3CH2OO + CH3CH2OH → 2 CH3CHO + HO2
Termination
The reaction is terminated when two radicals react with each other to form a stable product. For example, two hydroxyl radicals can react to form water.
OH → H2O
Two peroxyl radicals can react to form a dialkyl peroxide.
CH3CH2OO → CH3CH2OOCH2CH3
Applications
The reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2 finds practical applications in various industries and processes. One notable application is in the production of energy.
The combustion of ethanol, represented by the reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2, releases a significant amount of heat energy. This energy can be harnessed for various purposes, including heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Ethanol is considered a renewable energy source because it can be produced from plant biomass, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
Transportation
Ethanol is also used as a fuel additive or alternative to gasoline in internal combustion engines. By blending ethanol with gasoline, the fuel’s octane rating can be increased, reducing engine knocking and improving performance. Ethanol can also be used as a standalone fuel in vehicles specifically designed to run on ethanol, known as flex-fuel vehicles.
Chemical Industry, Ch3ch2oh + o2 balanced equation
The reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2 is employed in the chemical industry for the production of various chemicals. Acetaldehyde, an important intermediate in the production of plastics, synthetic rubber, and other chemicals, is synthesized through the oxidation of ethanol.
Research Directions
Ongoing research explores potential future applications and advancements related to the reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2. One area of interest is the development of more efficient catalysts to enhance the reaction’s selectivity and yield. Another research direction involves investigating the use of ethanol as a fuel source in fuel cells, offering the potential for clean and sustainable energy generation.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element remains constant throughout a reaction, reflecting the law of conservation of mass. It allows us to accurately predict the quantities of reactants and products involved, providing a quantitative understanding of the reaction.
What are the reactants and products in the reaction between CH3CH2OH and O2?
The reactants are CH3CH2OH (ethanol) and O2 (oxygen gas). The products are CO2 (carbon dioxide) and H2O (water).
What are the optimal reaction conditions for the combustion of ethanol?
The optimal conditions for complete combustion of ethanol involve a sufficient supply of oxygen and a temperature high enough to initiate the reaction. Typically, this occurs in the presence of a flame or spark.
