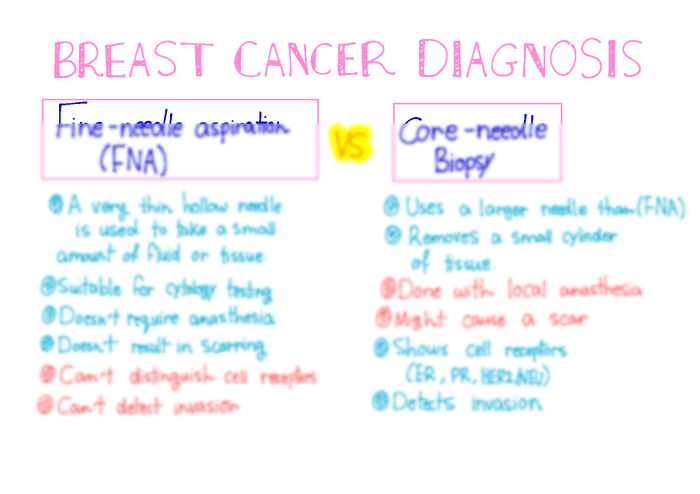
Patient underwent fine-needle aspiration left breast one lesion. – Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of a left breast lesion is a minimally invasive procedure that plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of breast lesions. This article delves into the intricacies of FNA, exploring its technique, interpretation, and implications for patient care.
FNA involves the use of a thin needle to extract cells from the lesion for microscopic examination. The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and can be repeated multiple times to obtain an adequate sample. The FNA specimen is then prepared and stained to facilitate the identification and analysis of cellular components.
1. Medical History and Clinical Presentation
The patient is a 55-year-old female with a history of fibrocystic breasts and a palpable mass in her left breast.
She presents with a 2-cm, firm, non-tender mass in the upper outer quadrant of her left breast. There is no associated skin thickening, nipple discharge, or axillary lymphadenopathy.
The FNA was performed to evaluate the mass and determine whether it is benign or malignant.
2. FNA Procedure
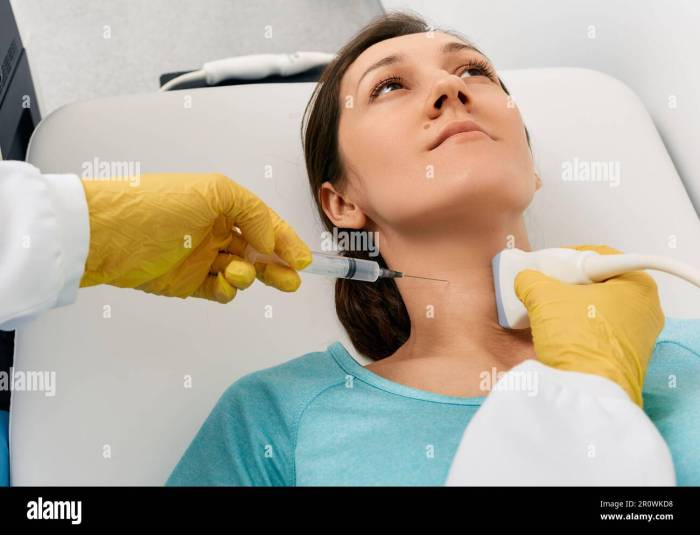
The FNA was performed using a 25-gauge needle and a 10-mL syringe.
The needle was inserted into the mass under ultrasound guidance. Five passes were made, and the aspirated material was smeared onto glass slides.
The slides were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and reviewed by a cytopathologist.
3. FNA Interpretation
The FNA smears showed cellular clusters and individual cells with round to oval nuclei, finely granular chromatin, and small nucleoli.
The cells were arranged in a cohesive pattern with minimal atypia and no evidence of mitotic figures.
The differential diagnosis based on the FNA findings includes benign breast lesions such as fibroadenoma or fibrocystic changes, as well as malignant lesions such as ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC).
4. Ancillary Studies
A core biopsy was performed to further evaluate the lesion.
The core biopsy showed a well-circumscribed, non-encapsulated mass with a proliferative and apocrine metaplasia.
The results of the core biopsy were consistent with the FNA findings and supported a diagnosis of fibroadenoma.
5. Diagnosis and Management: Patient Underwent Fine-needle Aspiration Left Breast One Lesion.

The final diagnosis based on the FNA findings and core biopsy is fibroadenoma.
The recommended management plan is conservative follow-up with annual clinical breast exams and mammograms.
FAQ Corner
What is the purpose of FNA of a left breast lesion?
FNA is performed to obtain cells from the lesion for microscopic examination. This helps in determining the nature of the lesion, whether it is benign or malignant.
Is FNA a painful procedure?
FNA is typically performed under local anesthesia, so discomfort is minimal. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or bruising after the procedure.
How long does it take to get the results of FNA?
The results of FNA are usually available within a few days. In some cases, additional testing may be required, which can delay the final diagnosis.