Name the property of equality that justifies this statement – The property of equality is a fundamental principle in mathematics that governs the behavior of equations and relationships. It states that if two expressions are equal to a third expression, then they are equal to each other. This property underpins the entire structure of mathematics and is essential for logical reasoning and problem-solving.
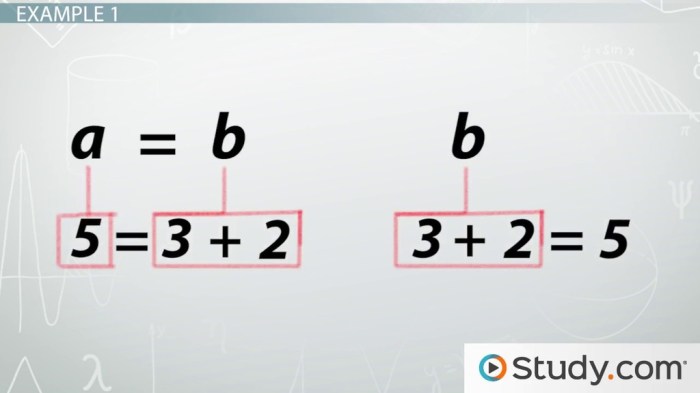
The property of equality is often used to justify statements and derive new conclusions. For instance, if we know that A = B and B = C, then we can conclude that A = C by the property of equality.
Property of Equality

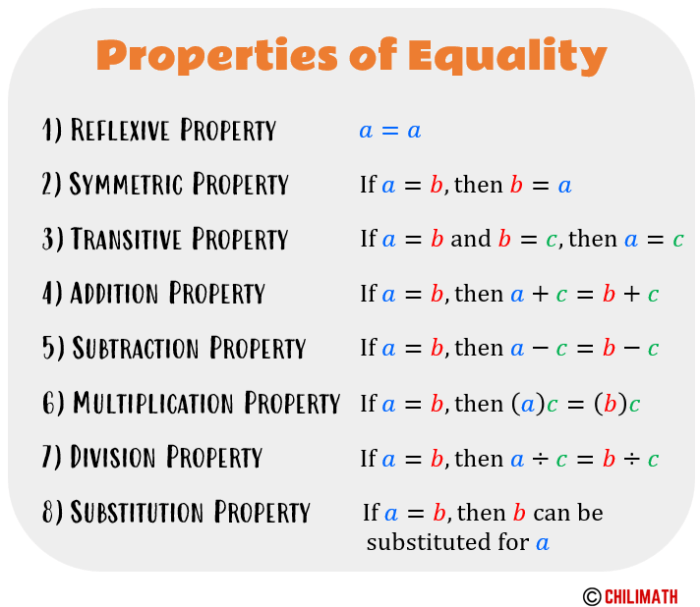
The property of equality states that if two expressions are equal to the same expression, then they are equal to each other. This property is fundamental to mathematics and is used to justify a wide variety of statements.
Examples of the Property
- If a = b and b = c, then a = c.
- If x + y = z and z = w, then x + y = w.
- If 2x = 10 and 10 = 5y, then 2x = 5y.
Methods of Justification: Name The Property Of Equality That Justifies This Statement
There are several methods that can be used to justify the property of equality. One common method is the substitution method. This method involves substituting one expression for another in an equation and then simplifying the equation until it is clear that the two expressions are equal.
Another method of justification is the proof by contradiction. This method involves assuming that the property of equality is false and then showing that this assumption leads to a contradiction. This contradiction proves that the assumption must be false, and therefore the property of equality must be true.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
- Substitution method:This method is relatively easy to use and can be applied to a wide variety of problems.
- Proof by contradiction:This method is more difficult to use than the substitution method, but it can be used to prove more general statements.
Examples of Applications
The property of equality is used to justify a wide variety of statements in mathematics. Some common examples include:
- The Pythagorean theorem: This theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This theorem can be justified using the property of equality.
- The distributive property: This property states that the product of a number and a sum is equal to the sum of the products of the number and each of the addends. This property can be justified using the property of equality.
Analysis of How the Property is Applied, Name the property of equality that justifies this statement
In each of these examples, the property of equality is used to show that two expressions are equal to each other. This allows us to make conclusions about the relationships between different mathematical objects.
Impact of the Property
The property of equality is a fundamental property of mathematics. It is used to justify a wide variety of statements and is essential for mathematical reasoning and problem-solving.
The property of equality also contributes to the development of logical thinking. By understanding the property of equality, students learn to identify and justify logical relationships between different statements.
Additional Considerations
There are a few limitations to the property of equality. For example, the property of equality does not apply to expressions that contain variables. Additionally, the property of equality does not apply to expressions that contain inequalities.
Despite these limitations, the property of equality is a powerful tool that can be used to justify a wide variety of statements in mathematics.
Quick FAQs
What is the property of equality?
The property of equality states that if two expressions are equal to a third expression, then they are equal to each other.
How is the property of equality used to justify statements?
The property of equality can be used to justify statements by showing that two expressions are equal to a third expression. For example, if we know that A = B and B = C, then we can conclude that A = C by the property of equality.