Embark on an atomic odyssey with atomic structure atoms inside out worksheet answers, an illuminating guide that unravels the enigmatic world of atoms, the fundamental building blocks of our universe. Prepare to delve into the heart of matter, deciphering the intricate structure of protons, neutrons, and electrons that orchestrate the symphony of chemical reactions.
Within the nucleus, protons and neutrons reside, each playing a pivotal role in defining an atom’s identity. Venture beyond the nucleus and encounter the electron cloud, a dynamic realm where electrons dance in their designated shells and subshells, governed by the enigmatic principles of quantum mechanics.
Introduction to Atomic Structure: Atomic Structure Atoms Inside Out Worksheet Answers
Atomic structure refers to the arrangement of subatomic particles within an atom. These particles include protons, neutrons, and electrons. Understanding atomic structure is crucial for comprehending the behavior of atoms and the chemical reactions they participate in.
Components of an Atom
Nucleus, Atomic structure atoms inside out worksheet answers
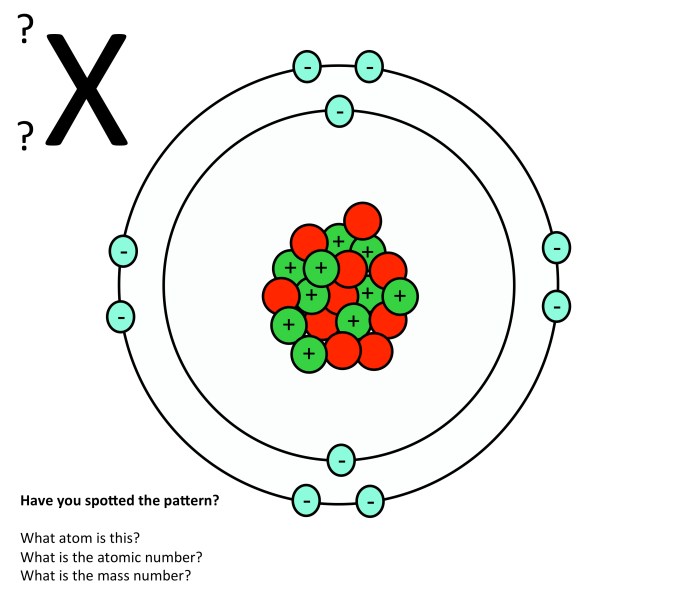
The nucleus is the central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles, while neutrons are neutral particles. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which identifies the element.
Electron Cloud
Surrounding the nucleus is the electron cloud, a region where electrons are found. Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels called shells.
Electron Configuration
Electron Shells and Subshells
Electron shells are designated by numbers (n = 1, 2, 3, …). Each shell can accommodate a specific number of electrons: 2 in the first shell, 8 in the second shell, and so on.
Within each shell are subshells, denoted by letters (s, p, d, f). Each subshell can hold a certain number of electrons: s subshells hold 2 electrons, p subshells hold 6 electrons, d subshells hold 10 electrons, and f subshells hold 14 electrons.
Aufbau Principle and Hund’s Rule
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. Hund’s rule states that when filling orbitals of equal energy, electrons occupy separate orbitals with parallel spins.
Atomic Properties
Atomic Radius
Atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. It generally increases down a group (column) and decreases across a period (row) of the periodic table.
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group of the periodic table.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It generally increases across a period and decreases down a group of the periodic table.
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends refer to the systematic changes in atomic structure and properties across the periodic table. These trends can be used to predict the properties of elements and their behavior in chemical reactions.
- Atomic radius increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Applications of Atomic Structure
Chemistry
Understanding atomic structure is essential for understanding chemical bonding, chemical reactions, and the properties of molecules.
Physics
Atomic structure plays a crucial role in nuclear physics, quantum mechanics, and the development of atomic and molecular spectroscopy.
Materials Science
Knowledge of atomic structure is vital for designing and developing new materials with specific properties, such as semiconductors, superconductors, and nanomaterials.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of atomic structure?
Atomic structure dictates the chemical properties and behavior of elements, enabling scientists to predict reactivity, understand bonding, and design new materials.
How does the electron cloud influence atomic properties?
The electron cloud determines an atom’s size, ionization energy, and electronegativity, shaping its interactions with other atoms and molecules.
What is the role of the nucleus in atomic structure?
The nucleus houses protons and neutrons, defining the atomic number and mass, and influencing the stability and radioactive properties of the atom.