Assignment 3 – Cloud Droplets and Raindrops embarks on a captivating journey into the realm of cloud microphysics, unraveling the intricate processes that govern the formation, growth, and interaction of these atmospheric particles. This exploration delves into the fundamental mechanisms underlying cloud droplet and raindrop dynamics, shedding light on their pivotal role in cloud and precipitation processes.
As we delve into the intricacies of cloud microphysics, we will uncover the factors that influence the size, distribution, and interactions of cloud droplets and raindrops. We will examine the processes of coalescence and collision-coalescence, which play a crucial role in raindrop formation.
Furthermore, we will explore the significance of updrafts and downdrafts in shaping the growth and trajectory of raindrops.
Cloud Droplets
Cloud droplets are tiny water droplets that form the visible part of clouds. They are formed when water vapor condenses around condensation nuclei, which are particles suspended in the atmosphere such as dust, smoke, or sea salt. The size and distribution of cloud droplets are influenced by factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of ice crystals.
Role of Condensation Nuclei
Condensation nuclei provide a surface for water vapor to condense on. The size and type of condensation nuclei can affect the size and number of cloud droplets that form. For example, larger condensation nuclei tend to produce larger cloud droplets.
Factors Influencing Size and Distribution
- Temperature: Higher temperatures lead to smaller cloud droplets.
- Humidity: Higher humidity leads to larger cloud droplets.
- Ice crystals: The presence of ice crystals can lead to the formation of smaller cloud droplets.
Raindrops
Raindrops are larger water droplets that fall from clouds. They are formed through a process called coalescence, where smaller cloud droplets collide and merge together. The size and shape of raindrops are determined by factors such as the rate of coalescence, the size of the cloud droplets, and the presence of updrafts and downdrafts.
Process of Formation
Coalescence occurs when cloud droplets collide with each other and stick together. This process is more likely to occur when the cloud droplets are large and have a high liquid water content.
Factors Influencing Size and Shape
- Rate of coalescence: A higher rate of coalescence leads to larger raindrops.
- Size of cloud droplets: Larger cloud droplets are more likely to coalesce.
- Updrafts and downdrafts: Updrafts can keep raindrops suspended in the cloud, allowing them to grow larger. Downdrafts can cause raindrops to fall out of the cloud.
Relationship between Cloud Droplets and Raindrops
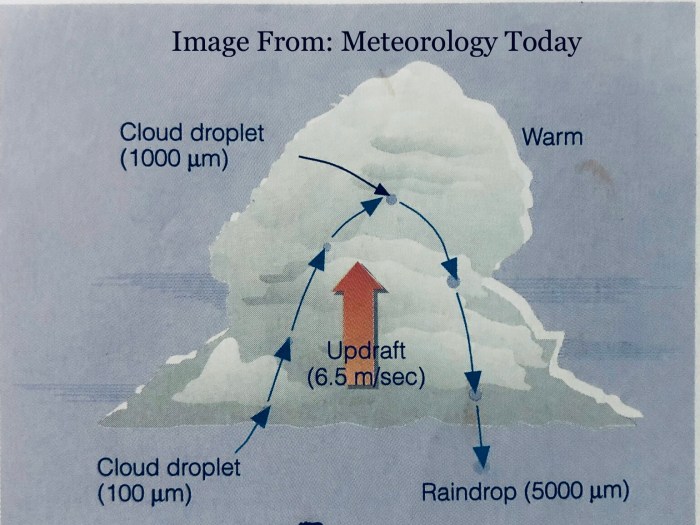
Cloud droplets and raindrops are part of a continuous spectrum of water droplets in clouds. The transition from cloud droplets to raindrops occurs when the cloud droplets become large enough to overcome the drag force of the air and fall out of the cloud.
Conditions for Raindrop Formation
- Sufficient cloud droplet size: The cloud droplets must be large enough to coalesce.
- High liquid water content: The cloud must have a high liquid water content to provide enough water for coalescence.
- Updrafts and downdrafts: Updrafts can keep raindrops suspended in the cloud, allowing them to grow larger. Downdrafts can cause raindrops to fall out of the cloud.
Impact of Cloud Droplet Size Distribution
The size distribution of cloud droplets can affect the formation of raindrops. A cloud with a wide range of cloud droplet sizes is more likely to produce raindrops than a cloud with a narrow range of cloud droplet sizes.
Cloud Microphysics: Assignment 3 – Cloud Droplets And Raindrops

Cloud microphysics is the study of the physical processes that occur within clouds. These processes include the formation, growth, and precipitation of cloud particles. Cloud microphysics is important for understanding cloud and precipitation processes, and for developing numerical weather prediction models.
Types of Cloud Particles, Assignment 3 – cloud droplets and raindrops
- Cloud droplets: Small water droplets that form the visible part of clouds.
- Ice crystals: Small ice particles that form in clouds at cold temperatures.
- Graupel: Soft, rimed ice particles that form when supercooled water droplets freeze on ice crystals.
- Hail: Hard, layered ice particles that form when graupel is carried up and down through the cloud by updrafts and downdrafts.
Interactions between Cloud Particles
Cloud particles interact with each other through processes such as coalescence, collision-coalescence, and riming. These processes can lead to the formation of larger cloud particles and precipitation.
Role in Numerical Weather Prediction Models
Cloud microphysics is an important component of numerical weather prediction models. These models use cloud microphysics to predict the formation, growth, and precipitation of cloud particles. This information is used to forecast the weather and to study the effects of climate change.
Cloud and Precipitation Observations

Cloud and precipitation observations are important for understanding cloud and precipitation processes, and for validating numerical weather prediction models. These observations can be made using a variety of instruments, including radar, disdrometers, and satellites.
Radar Measurements
Radar measures the reflectivity of precipitation particles. The reflectivity is proportional to the size and number of precipitation particles. Radar can be used to estimate the amount and intensity of precipitation.
Disdrometer Measurements
Disdrometers measure the size and shape of precipitation particles. This information can be used to determine the type of precipitation and to estimate the amount of precipitation.
Challenges and Limitations
Cloud and precipitation observations can be challenging and limited by factors such as the presence of multiple precipitation types, the vertical structure of clouds, and the availability of instruments.
FAQ Section
What are the key factors that influence the size and distribution of cloud droplets?
The size and distribution of cloud droplets are primarily influenced by the availability of condensation nuclei, temperature, and humidity.
How do raindrops form through coalescence and collision-coalescence?
Coalescence occurs when smaller cloud droplets collide and merge to form larger droplets. Collision-coalescence occurs when larger droplets collide with smaller droplets and capture them, leading to further growth.
What role do updrafts and downdrafts play in raindrop growth?
Updrafts carry cloud droplets and raindrops upward, providing them with more time to grow through coalescence and collision-coalescence. Downdrafts, on the other hand, can disrupt the growth process and lead to the evaporation of raindrops.